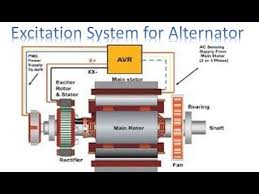
Excitation Current is vital to get an alternator or generator. It’s in a position to create and maintain a voltage requirement for constant generation of electricity.
Here We’re currently talking Roughly large scale alternators of generators are used in other significant software and power plants. In this system, the Sophisticated automation process is utilized for distribution and control of excitation current.
What is excitation current of an Alternator or Generator
Already we know that for the generation of power, initially, a voltage is to be generated in the stator. By finishing the circuit, Using energy generated, energy shall flow. Our discussion is going to be that the stator is fixed, and the rotor is rotating. This type of arrangement is used for the majority of the alternator and generator. For the creation of electric voltage in a circuit, three things are needed –
1. Magnetic flux: Magnetic circuit is put in the rotor. Desired magnetic flux is created in the rotor by providing DC (Direct Current) into the rotor circuit. This Direct Current (DC) is known as excitation current. That is required to generate magnetic flux from the rotor circuit.
2. Conductor: Conductor is placed in the stator. It’s placed as the coils include of a lot of conductor for carrying capability concern.
3. Relative movement between the magnetic flux and conductor: Relative movement is availed through rotor combined with a prime mover which would function engine, turbine, etc..
So we can state that the current supplied to the rotor circuit to produce magnetic flux is known as the excitation current to get an alternator. This whole part is called the Exciter machine.
Should the excitation present to be fixed or flexible in Electric Alternator or Generator:
An alternator operates in Varying load condition and situations. And we know that during the performance, the alternator terminal voltage is to be kept constant. It can be fluctuating. Terminal voltage to remain the same or consistent, although the current might be changeable.
The excitation current is the current that creates the terminal voltage. Rating of excitation present controls the terminal voltage level. To maintain the terminal voltage fixed or constant, the excitation current is to be both variable and adjustable.
So, excitation has to be adjustable.
Source of excitation present in Electric Alternator or Generator:
The excitation current is supplied to the rotor using a device called Automatic Voltage Regulator (AVR). The source of the excitation current varies from design and the manufacturer. In some cases, the excitation present would be provided from a generator or an external battery.
In some cases, an Additional winding is placed in the primary winding of stator, which creates and provides the current to the Automatic Voltage Regulator (AVR).
The origin of excitation current is not directly Direct current (DC). It is Alternating current ( AC). The Alternating current is then converted into Direct current (DC) before fed into the rotor circuit.
In some cases, the arrangement is made to cope up passing conditions. These are boost link with the amount of excitation current boosted.
The Way the excitation current is regulated from Electric Alternator or Generator:
The excitation current is provided from the device Named AVR (Automatic Voltage regulator). It governs the excitation current thus controls the generator terminal voltage.
1. AVR (Automatic Voltage regulator) is fed with Alternating current (AC).
2. The source of Alternating varies from style to style and from different arrangement.
3. AVR (Automatic Voltage regulator) is a sophisticated device that supply excitation current by real-time calculation. It carries data input from several sources, for example, terminal voltage, load state, load demand, etc..
How excitation current is provided to the rotor circuit at Electric Alternator or Generator:
We know that the excitation present is Only the Direct current (DC) supplied to the rotor circuit to create magnetic flux. And, it’s needed to be adjustable. Excitation current from outside is to be provided into the rotor that is rotating. This is accomplished through the two method brush excitation system and Static excitation system.
Types of excitation system in an Alternator
The two excitation systems are Brushless Excitation and excitation.
As we already know, the rotor is rotating and stator. The Field circuit is placed on the rotor, which is moving. Direct current ( DC) is to be supplied to this rotor circuit for producing a magnetic field. Here lies the most critical challenge. To provide this current. There are two forms of arrangement.
1: Brushless Excitation system in Alternator or Generator
This circumstance, the induction process is used. At AC excitation current is converted into DC by rectifier collection. Subsequently, this Direct current (DC) is fed into a magnetic circuit that produces a magnetic field. The rotor includes a 3 stage. Thus induction current is generated from the rotor. Then this present is converted to Direct current (DC) from rectifier arrangement. Afterward, this Direct current is fed into the magnetic circuit. In this method, there is no physical connection between the external excitation supply and the rotor.
When a Brushless excitation process is utilized, there is a rotating machine coupled to the generator non driven shaft, providing the excitation current. This machine, known as exciter machine, has
1. in the rotor a 3-phase winding and
2. in the stator that an excitation (area ) winding connected to direct current.
Therefore, An alternating current is induced into the rotor winding.
The Expand alternating current at the terminals of this rotating 3-phase winding must be rectified. This happens using a diode bridge fixed on so and the shaft. The consequent current is fed directly to the generator’s rotor winding.
The direct current for the stator winding of the exciter is provided through
1. the generator terminals,
2. Through an excitation transformer and
3. A rectifier collection.
Edge of brush excitation system in Alternator or Generator
A Brush excitation system has a comparative extended response characteristic (time constant), when compared with the static excitation system.
2: Static excitation system in Alternator or Generator
In This case, direct current is fed into the magnetic circuit. There is physical contact between the external circuit to the rotor. The flow is transferred through a slip ring arrangement. This Immediate current ( DC) is generally transformed from Alternating current ( AC). It’s done in other place or the panel. But Immediate is supplied to the Rotor circuit.
The Excitation current has to be moved on the rotor through brushes from the excitation system. The brushes move the direct current via two isolated slip bands into the rotor. The brush equipment is mounted at this generator’s finish; the components are covered with an air-cooled casing.
Edge of Static excitation system in Alternator or Generator:
A Static excitation system has a fast response time in case of an essential sudden Alter of the exciter current when compared with the brush system.